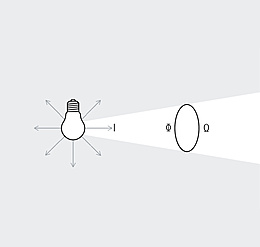
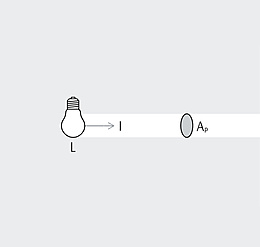
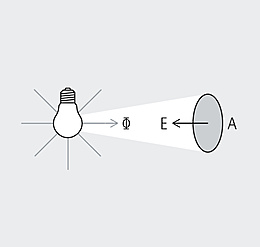
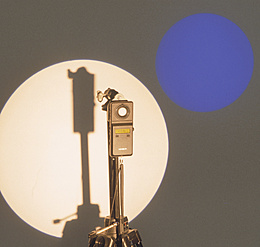
The photometric law of distance describes the relationship between the illuminance and the distance of the measuring plane to the light source. Illuminance recedes with the square of the distance from the light source.
A1 = Ω x r2
A2 = Ω x (2 x r2)2 = 4 x R x r2 = 4 x A1