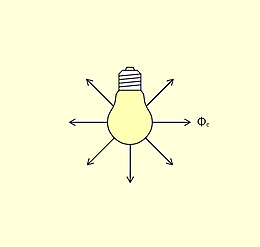
Luminous intensity is a measure of the luminous flux emitted per solid angle.
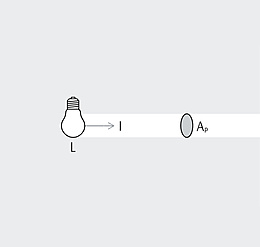
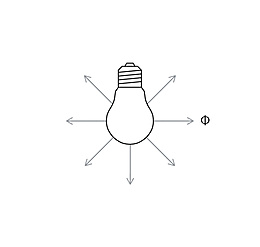
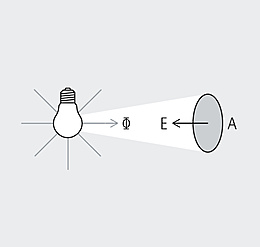
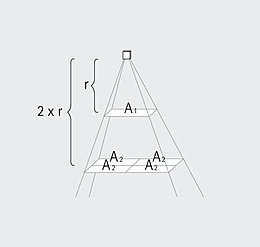
Luminous intensity (I) is the luminous flux (Φ) emitted by a light source per solid angle (Ω), the unit of measure being the candela (cd). It is one of the seven basic quantities of the international system of units. Unlike kilograms or seconds though, luminous intensity involves human perception. The luminous intensity distribution body describes the spatial distribution of the luminous intensity of a light source. A section through this body gives the light distribution curve.
An ideal, point-shaped light source radiates its luminous flux uniformly in all directions of the room and its luminous intensity is the same in all directions. In practice however, the spatial distribution of luminous flux is always non-uniform. This is partly due to the construction of the light sources and partly due to specific control by the luminaire. It therefore makes sense to specify a measure of the spatial distribution of the luminous flux, i.e. the luminous intensity of the light.